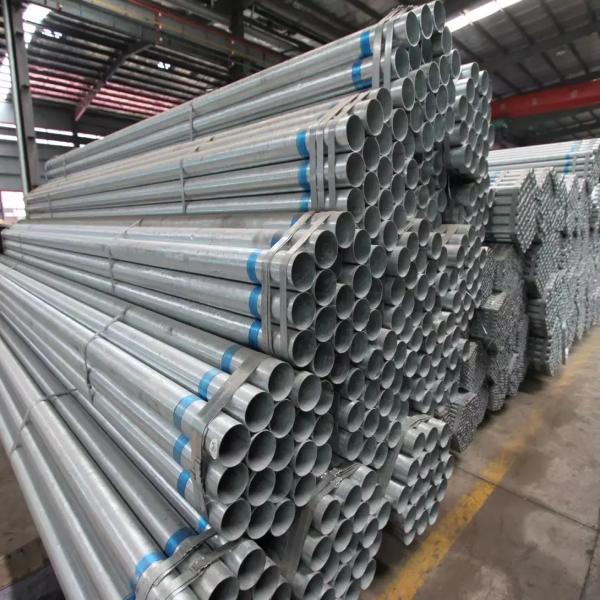
Overview of Stainless Welded Pipe Manufacturing Process: Forming: Stainless steel strips or plates are formed into a cylindrical shape. Welding: The edges of the formed cylinder are welded together using various welding techniques such as TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas), MIG (Metal Inert Gas), or submerged arc welding. Heat Treatment: Post-weld heat treatment may be applied to relieve stresses and improve corrosion resistance. Finishing: Pipes are then cut to desired lengths, undergo surface treatment (pickling/passivation), and inspection. Advantages: Cost-Effective: Lower production costs compared to seamless pipes. Versatility: Available in a wide range of sizes and thicknesses. Strength: Welded joints can be as strong as the base material when performed correctly. Customization: Easily tailored to specific dimensional and application requirements. Applications: Construction: Structural supports, handrails, and architectural elements. Industrial: Process piping, heat exchangers, and machinery components. Transportation: Automotive exhaust systems, railings, and pipelines. Utilities: Water and gas distribution systems, sanitary applications. Standards and Specifications: ASTM A312: Standard specification for seamless, welded, and heavily cold worked austenitic stainless steel pipes. ASTM A358: Specification for electric-fusion-welded austenitic chromium-nickel stainless steel pipe for high-temperature service and general corrosive service. DIN 17457: Welded circular tubes of austenitic corrosion-resistant stainless steel. Types of Stainless Steel: Austenitic: Commonly used grades include 304 (L), 316 (L); excellent corrosion resistance and formability. Ferritic and Martensitic: Grades like 409, 410, 430; good mechanical properties and moderate corrosion resistance. Duplex and Super Duplex: Grades like 2205, 2507; higher strength and improved resistance to stress corrosion cracking. Conclusion: Stainless welded pipes offer a practical and economical solution for various industrial and commercial applications. Their versatility, strength, and customization options make them suitable for diverse environments where corrosion resistance, durability, and structural integrity are critical.

 Sign in with Google
Sign in with Google
 Sign in with Facebook
Sign in with Facebook

 Sign in with Google
Sign in with Google












































 USD or choose a different currency.
USD or choose a different currency._1727168586.png)

) (1)_1727158160.png)


 (4)_1729176674.png)
